|
Introduction
CableHome™ is a new home networking
architecture that has the potential to be an important step in
the evolution of communications for the home. It was sponsored
by CableLabs® which is an organization that supports the common
development interests of the cable operators. As with the cable
modem standard DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification),
the operators commitment to only buy and support equipment that
is certified by CableLabs is a powerful influence in determining
the direction for the industry.
The objective of the CableHome™ architecture is to provide
a variety of new services to residential customers, simplify the
management the home network, and protect copyrighted information
from being diverted to other uses. Within the residence, the CableHome
architecture is designed to be independent of the underlying network
technologies such as Ethernet, wireless, HomePNA, and HomePlug.
While not all services can operate on all LAN technologies, the
desire to let market forces decide on the most cost effective
systems allows for an evolution of the network.
The initial version of CableHome architecture,
CableHome 1.0, describes the functions needed to implement the
security, management, and network protection services of the architecture.
This should enable the benefits of networks used in businesses
to migrate into the home environment The CableHome functions are
implemented in the Home Access (HA) device shown in Figure 1.
The HA device is a combination of a Cable Modem (CM) and additional
features known as Portal Services (PS). The HA device can be a
single unit or allows for using existing DOCSIS 1.1 Cable Modems
and a new PS unit connected together.
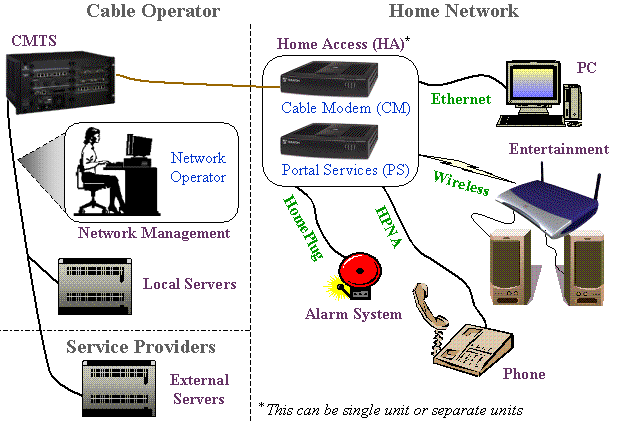
Figure 1. Overview of CableHome 1.0
The HA device
is a combination of a Cable Modem (CM) and additional features
known as Portal Services (PS). The HA device can be a single unit
or it can be implemented using an existing DOCSIS 1.1 Cable Modem
and a new PS unit connected together. The functions that are implemented
in the Portal Service are:
-
Address Translation
-
Address Management
-
Remote management
-
Support Quality of Service for the user's data
-
Security features to protect the user
-
Security of the content providers data to the user
Today, people wanting to implement a
home network with these features buy units that implement Network
Address Translation (NAT), address servers (DHCP), firewalls,
and routers. It is normally very difficult for people not familiar
with networking to install this equipment and diagnose problems
when they occur. In a business environment, specialists are employed
to perform these functions but this is not feasible for the average
home network.
The CableHome architecture implements
the desirable features mentioned without the complexity for the
user. It also overcomes many of the limitations of the traditional
NAT while ensuring the needs of content providers are protected.
In order to offer new services, the provider must be assured:
-
that the data is going to the
specified user and not somebody masquerading as that user.
-
that the data is protected (copied by the user or someone
listening to the data)
-
that the quality of the data stream is acceptable (low
error rate, not visibly jerky, not too long a delay if it interactive).
-
that the user cannot later say they don't want to pay
for the service because the data stream did not arrive or was
of poor quality.
CableHome helps achieve these objectives
because it gathers information about the network that is attached
to the HA. The HA collects information on error rates, manages
bandwidth on home networking technologies that support Quality-of-Service
(QoS) delivery such as HomePNA and the IEEE 802.11 wireless technology.
The complete CableHome 1.0 specification
can be found at www.cablelabs.com/cablehome/specifications.html.
Portal Services
The CableHome Portal Services feature
is composed of several different functions. A block diagram of
the various PS functions is shown in Figure 2. A brief explanation
of each function is described below.
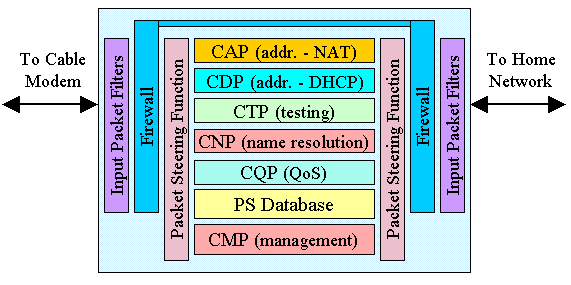
Figure 2. Block diagram of the PS functions
Note:
CAP = CableHome Address Portal
CDP = CableHome DHCP Portal
CTP = CableHome Testing Portal
CNP = CableHome Naming Portal
CQP = CableHome Quality of Service Portal
CMP = CableHome Management Portal
CableHome Address Portal (CAP)
The CAP creates address translation mappings
between the External Network and Home Network. Its basic functions
are:
-
Shares a single external IP
address with many home devices (Network Address Translation -
NAT).
-
Decides which packets from the home network need to go
to the external network which helps to preserve upstream bandwidth.
-
Provides a Passthrough function, which allows packets
for a particular device not to be translated by the NAT or altered
by Application Layer Gateway (ALG) functions.
CableHome DHCP Portal (CDP)
The CDP provides the address assignment
functions (e.g. those transmitted via DHCP) including a server
for the devices on the home network and a client for the external
network. This allows home devices to get an IP address, the address
of the gateway to get out of the home, an the address of a DNS
server which translates a site name into an IP address, and a
variety of other network configuration parameters.
CableHome Naming Portal (CNP)
The CableHome Naming Portal is a service
running in the PS that provides a simple DNS server for LAN IP
Devices in the home. Its basic functions are:
-
Provide Domain Name Service
(DNS) from a server in the PS to DNS clients within home devices,
even during cable connection outages.
-
Enable subscribers to refer to local devices via intuitive
device names rather than by IP address.
-
Refer LAN DNS clients to Headend DNS servers, for resolution
of non-local hostnames.
-
Provide easy DNS service recovery upon re-establishment
of cable connectivity after an outage.
CableHome Quality of Service Portal (CQP)
CQP provides
the environment to enable home networking applications to utilize
PacketCable and DOCSIS QoS resources. These resources provide
a management mechanism that prioritizes data session to support
real-time application traffic, such as VoIP, A/V streaming, and
video gaming, by reducing packet latency and jitter delays. Its
basic functions are:
-
Enable home networking applications
to establish prioritized data sessions between the CMTS and HA
device using PacketCable compliant messaging.
-
Facilitate design and field-testing leading to the manufacture
and interoperability of conforming hardware and software by multiple
vendors.
CableHome Management Portal (CMP)
The PS is managed from the external network
via the CMP, and to a large degree, this involves access to the
information in the PS Database. Management is used for initialization
and provisioning of the network elements, and diagnostics or status
of the LAN. Its basic functions are to:
-
Provide cable operators with
visibility to LAN IP Devices.
-
Provide cable operators with a minimum set of remote
diagnostic tools that will allow the cable operator to verify
connectivity between the Portal Services element and any home
networking device.
-
Provide cable operators with access, via the MIBs,
to internal data in the PS element and enable the cable operator
to monitor CableHome-specified parameters and to configure
or reconfigure CableHome-specified capabilities as necessary.
-
Provide a means for reporting exceptions and other events
in the form of SNMP messages to a local log or to the cable network.
The PS Database
The PS Database stores a myriad of data
relationships. The CMP provides the management interface (SNMP)
to the PS database. The CableHome functions within the PS enter
and revise data relationships in the PS Database. Additionally,
the CableHome Functions within the PS may retrieve information
from the PS Database that is maintained by other CableHome Functions
within the PS.
CableHome Security Portal (CSP)
The CSP acts as a security portal for
other HA elements. One of its primary functions is to forward
security messaging between Cable Operator's servers (including
the security server) and PacketCable applications. Its basic functions
are to:
-
provide security services, such
as authentication and key management for the PS element.
-
provide firewall functions to protect the home user from
network attacks
-
provide screening functions to prevent children from
getting to unauthorized sites.
CableHome Testing Portal (CTP)
The CTP (CableHome Test Portal) contains
the "remote tools" with which the NMS can collect further
LAN device information. The CTP is a local proxy used to interpret
and execute the remote fault/diagnostic class of SNMP messages
it receives from the cable operator. Its basic functions are to:
-
Enable LAN IP Device fault diagnostics
-
Enable visibility to LAN IP Devices
-
Enable LAN IP Device performance monitoring
Future Versions
The CableHome 1.0 specification is just
the initial version of the overall CableHome Architecture. While
this specification focuses on the Home Access device, there is
much more to the architecture. The complete CableHome Architecture
Framework Technical Report can be found at www.cablelabs.com/cablehome/specifications.html.
Shown in Figure 3 are some of the additional
elements that will be included in future versions of CableHome.
The HB device, known as a gateway, joins two of the home networks
both of which are compliant to the CableHome specification. For
networks that are not complaint with CableHome, an HC device,
known as a Boundary Point, performs the necessary buffering and
monitoring functions for the non-compliant networks.
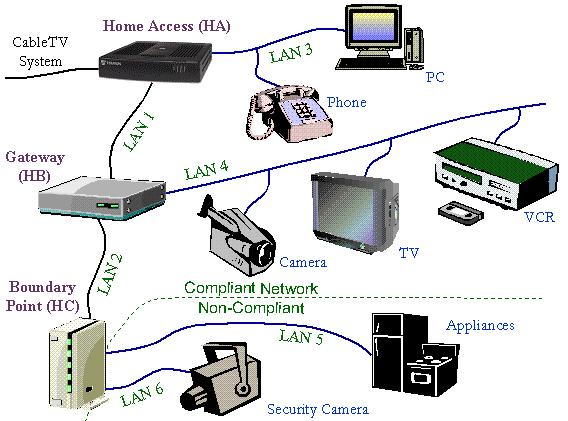
Figure 3. Overview of the CableHome Architecture
Thought has been given as to how a home
network may evolve and the architecture is flexible enough to
handle a variety of changes. As in today's business environment,
when LAN segments start being overloaded, there is point were
it makes sense to subdivide them. When that happens, typically
bridges or routers are used to separate these segments. In the
CableHome architecture, the generic device that isolates networks
is known as Gateway (GW) or HB device.
The GW may contain a bridge, router,
NAT, and other functions. It is more than a standard bridge or
router because it can be managed by the operator, can perform
network monitoring and testing. An HB can have one or more LAN
segments connected to it. In the above figure, LAN 4 is a network
consisting of AV devices and its large bandwidth requirements
for local transfer does not affect the data transfer of the PC
or other devices not on that segment.
Another CableHome device is a Boundary
Point (BP) or HC device. Normally the devices attached to LANs
managed by the operator have the TCP/IP protocol installed and
can participate in bandwidth reservation and provisioning. This
assumption is valid for many intelligent devices such as a PC
but there may be low cost devices that can't support the economics
of such a protocol. For this situation, the BP isolates these
low cost / low sophistication devices from CableHome compliant
networks.
The BP essentially acts like a translator
taking CableHome commands and translates them to appropriate commands
for that type of device. The desire is to support all types of
end devices, so the BP is defined only on the CableHome side,
and a BP manufacturer does whatever is necessary to act as an
agent for devices on non-compliant networks.
In Figure 3, inexpensive communications
technologies are required for "smart" appliances (LAN
5) or non-IP aware devices such as a security camera. If the user
chooses to have the home network configured and maintained by
the operator, these devices can be identified, and problems diagnosed
because of the intelligence of the BP.
More Information
CableHome uses DOCSIS (the cable modem
standard) to transmit information between the headend and the
home.
DOCSIS seminars:
 Overview - An overview of the components of a cable TV system.
Overview - An overview of the components of a cable TV system.
 The DOCSIS Protocol - A description of the messages
between the CMTS and the CM. This includes the mechanism to share
the coax, ranging and registration.
The DOCSIS Protocol - A description of the messages
between the CMTS and the CM. This includes the mechanism to share
the coax, ranging and registration.
 The DOCSIS Physical Layer - The downstream/upstream modulation and data rates.
The DOCSIS Physical Layer - The downstream/upstream modulation and data rates.
 Quality of Service (DOCSIS 1.1) - The changes to DOCSIS
1.0 to implement QoS.
Quality of Service (DOCSIS 1.1) - The changes to DOCSIS
1.0 to implement QoS.
In Summary:
-
CableHome will be an important home networking
technology because the Cable Operators will require its use
for customers to get enhanced content.
-
CableHome will accommodate existing and future
LAN technologies.
-
Existing NATs, Routers, and Bridges will need
to be enhanced to work with CableHome services.
-
CableHome 1.0 is the first version of the overall
CableHome architecture.
|

